You may have many questions about natural Resin Examples in your mind, Do you know what natural resin is?
In contrast to synthetic resin, which is produced chemically, natural resin is a resin product that comes from a plant. Human cultures have utilized natural resins for thousands of years; one illustrative example of this may be seen in Egypt, where mummified remains were prepared using resin. Natural resins are still used today for various purposes, from making perfume to preserving the bows of stringed instruments like violins and cellos.
Natural Resins Examples
A natural resin is distinguished by a few characteristics. The first is that it initially has a sticky, slightly gummy consistency before hardening with time. The second is water insoluble but soluble in alcohol and similar chemicals. Resins can be heated or treated in alcohol to soften them, then applied to something and allowed to dry, which is what makes them such useful materials. The resin won’t allow water entry after it has dried.

Sometimes, the basic natural resin is processed to eliminate the terpenes; in this instance, it is referred to as rosin. Bowstrings are treated with rosin, a type of natural resin. Some resins also referred to as gum resins or oleoresins, remain soft. Oleoresins may contain aromatic chemicals that cause them to be categorized as balsams, and gum resins combine the characteristics of gum and resin.
Incense and perfume both contain soft natural resin. One well-known soft resin that is famously mentioned in the Bible is frankincense. Like many other balsams, this aromatic resin has been utilized in Middle Eastern incense and perfumes for a very long period. Balsams from all over the world can also occasionally be found in personal care products, where they may be used for therapeutic purposes or just for their potent aroma.
Artificial and Natural Resins Examples
Amber is occasionally produced when natural resin turns into a fossil. It is possible to cut and polish this fully solid and cured kind of resin to create a dazzling translucent stone that can be any color from light yellow to deep orange. Some civilizations consider amber to have healing or therapeutic properties.
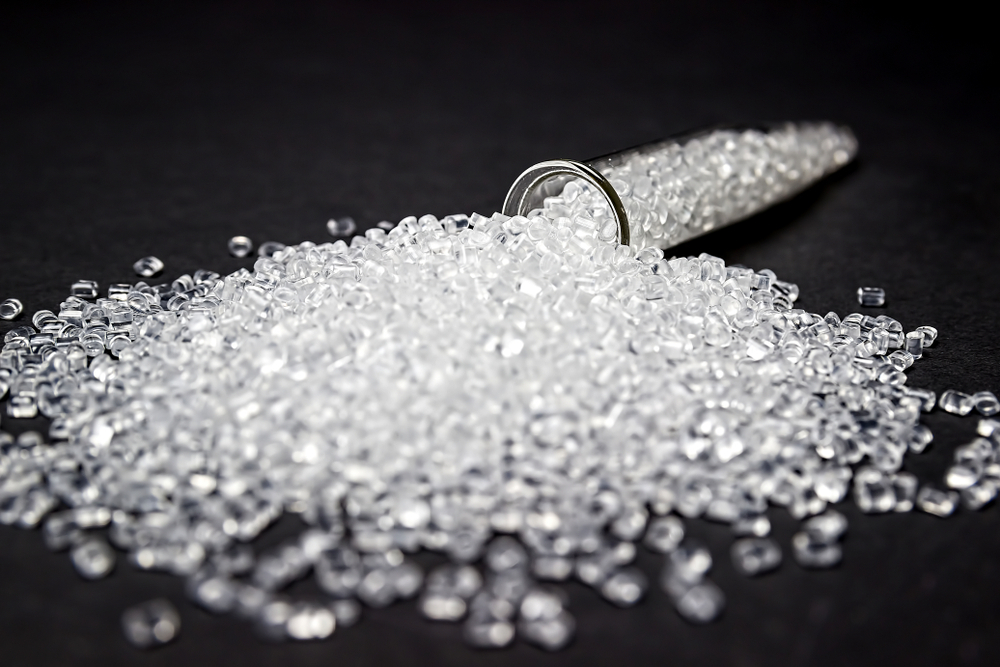

A broad category of artificial resin with some of the physical characteristics of natural resins but different chemical compositions is referred to as synthetic resins. Plastics and artificial resins cannot be distinguished with certainty.
Thermoplastic Resins Examples
The following are some examples of popular thermoplastic resins used today and the items they are used to make:
- PET bottles for soda and water
- Polypropylene – Containers for packaging
- Safety glass lenses made of polycarbonate
- PBT – Toys for kids
- Window frames made of vinyl
- Grocery bags made of polyethylene
- Plastic piping
- PEI – Armrests in airplanes
- Nylon – Shoes
Short, discontinuous fibers are frequently used in thermoplastic products as reinforcement. Carbon fiber is also used, but fiberglass is more typical. Although theoretically, a fiber-reinforced composite improves the mechanical properties but is not nearly as strong as continuous fiber-reinforced composites.
Thermosetting Resins Examples
FRP Composites, also known as traditional fiber-reinforced polymer composites, use a thermosetting resin as the matrix to hold the structural fiber securely in place. Typical thermoset resin examples are:
- Vinyl Resin
- Epoxy
- Phenolic
- Urethane
Polyester resin is currently the most popular thermosetting resin, followed by vinyl ester and epoxy. Thermosetting resins are well-liked because, while uncured, they are liquid at room temperature. This makes it possible to easily impregnate reinforcing fibers like Kevlar, carbon fiber, or fiberglass.
Bile Acid Resins Examples
The two most important bile acids produced in humans are cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid. Deoxycholic and lithocholic acids, which are formed from cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid, respectively, are secondary bile acid species that are produced as a result of the intestinal bacterial flora’s impact on primary bile acids (2).
Bile Acid-binding Resins Examples
What are bile acid-binding resins?
By preventing their absorption in the intestine, where more than 90% of bile acids are absorbed, bile acid-binding resins stop the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. Their primary application today is as adjunctive therapy for individuals with severe hypercholesterolemia brought on by elevated LDL-C.
Very Large Polymeric Cation Exchange Resins Examples
A resin or polymer that serves as a medium for ion exchange is known as an ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer. It is an insoluble matrix (or support structure) made from an organic polymer substrate, typically appearing as tiny (0.25-1.43 mm radius) microbeads that are white or yellowish in color.
The process is known as ion exchange because the beads are often porous, providing a wide surface area on and inside them where the trapping of ions takes place along with the concomitant release of other ions. Ion-exchange resin comes in many different varieties.
Cation Exchange Resins and Amino Resins Examples
By accelerating potassium loss through the stomach, cation-exchange resins are used to treat hyperkalemia, particularly when there is insufficient urine output or before dialysis (the most effective means of treating hyperkalemia). It also shows the Resins Examples in pharmacognosy.
Melamine formaldehyde and urea formaldehyde are two examples of amino resins. Amino resins are employed in the production of paper, coatings, adhesives, lamination, textile finishes, and molded plastics.
Where to Buy Resin?
Visit the resin store to buy resins online at a cheap price.
Final Words
Many plants naturally create resin as a defensive and healing mechanism. Terpenes, which are frequently found in resins and give them their distinct smell, give them a hydrocarbon base. They may also include other substances. Resins are gooey, sticky, and squishy when they are young. They become harder with time. Because the resin is sufficiently hard to be utilized in adhesives, paints, sealants, varnishes, and other products, this hardening is what makes them valuable to humans.
Hope this write-up has helped you to know about natural Resins Examples.
Read the pillar article to learn about all types of Resin Definitions, History, Types, Functions, Advantages, Disadvantages, and FAQ.